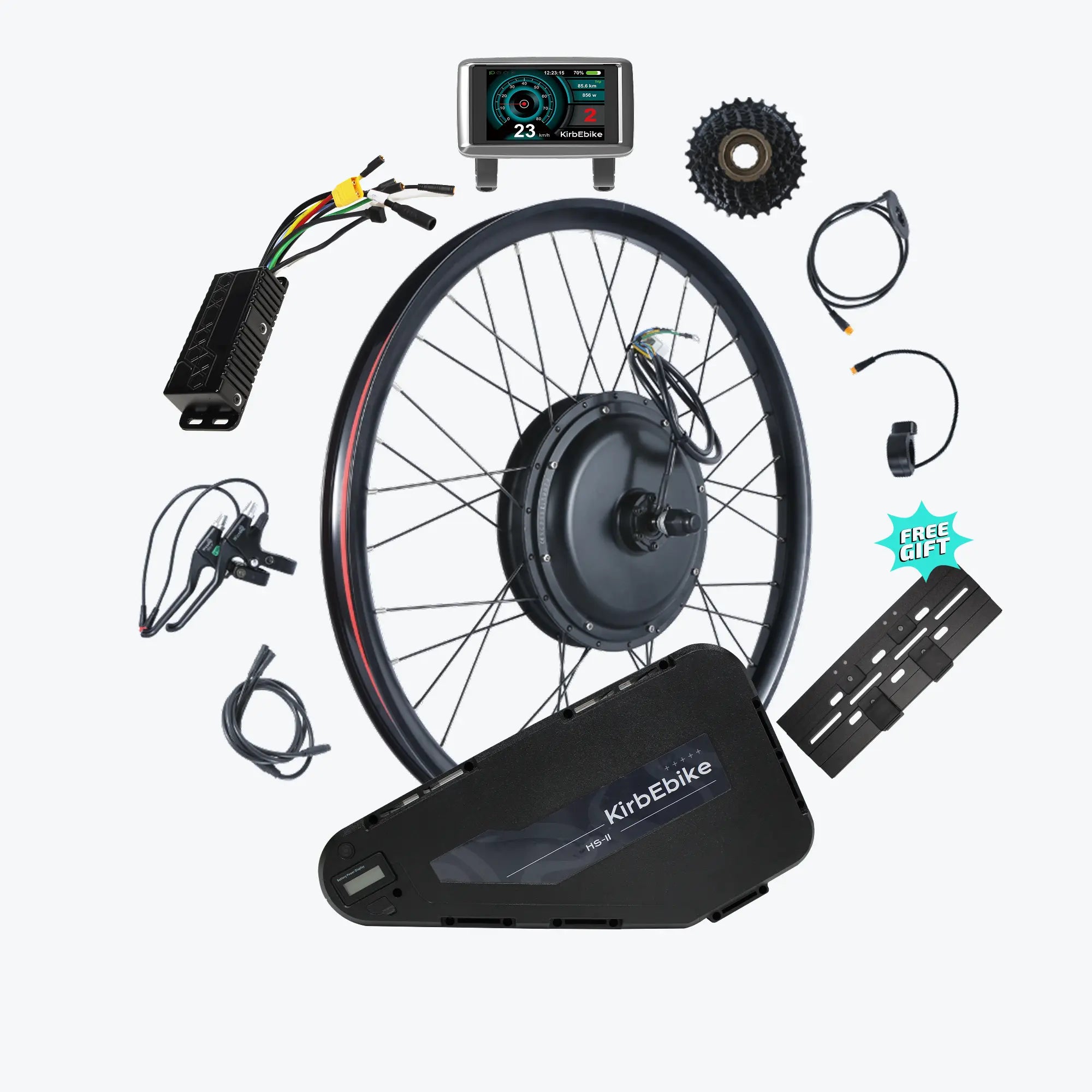
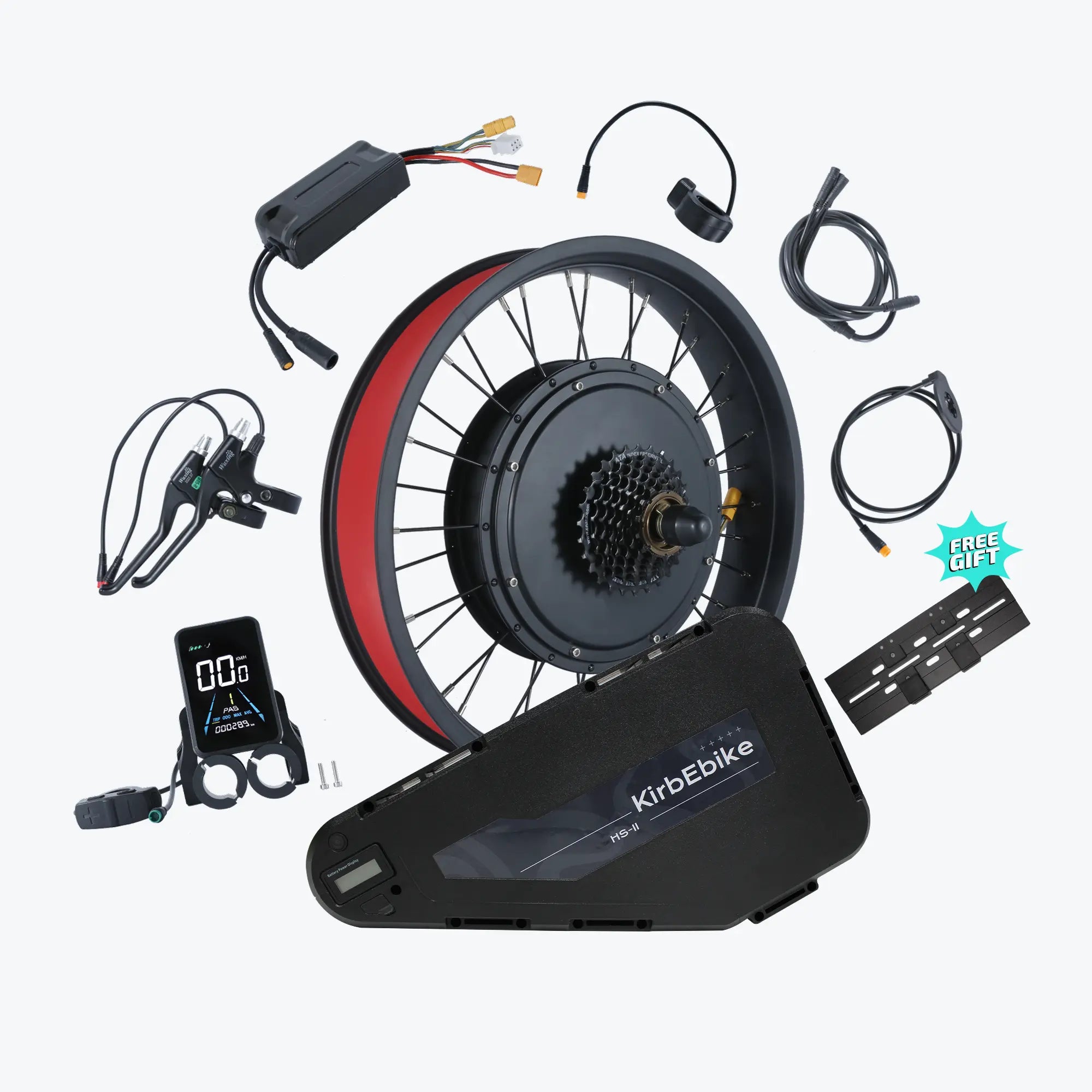
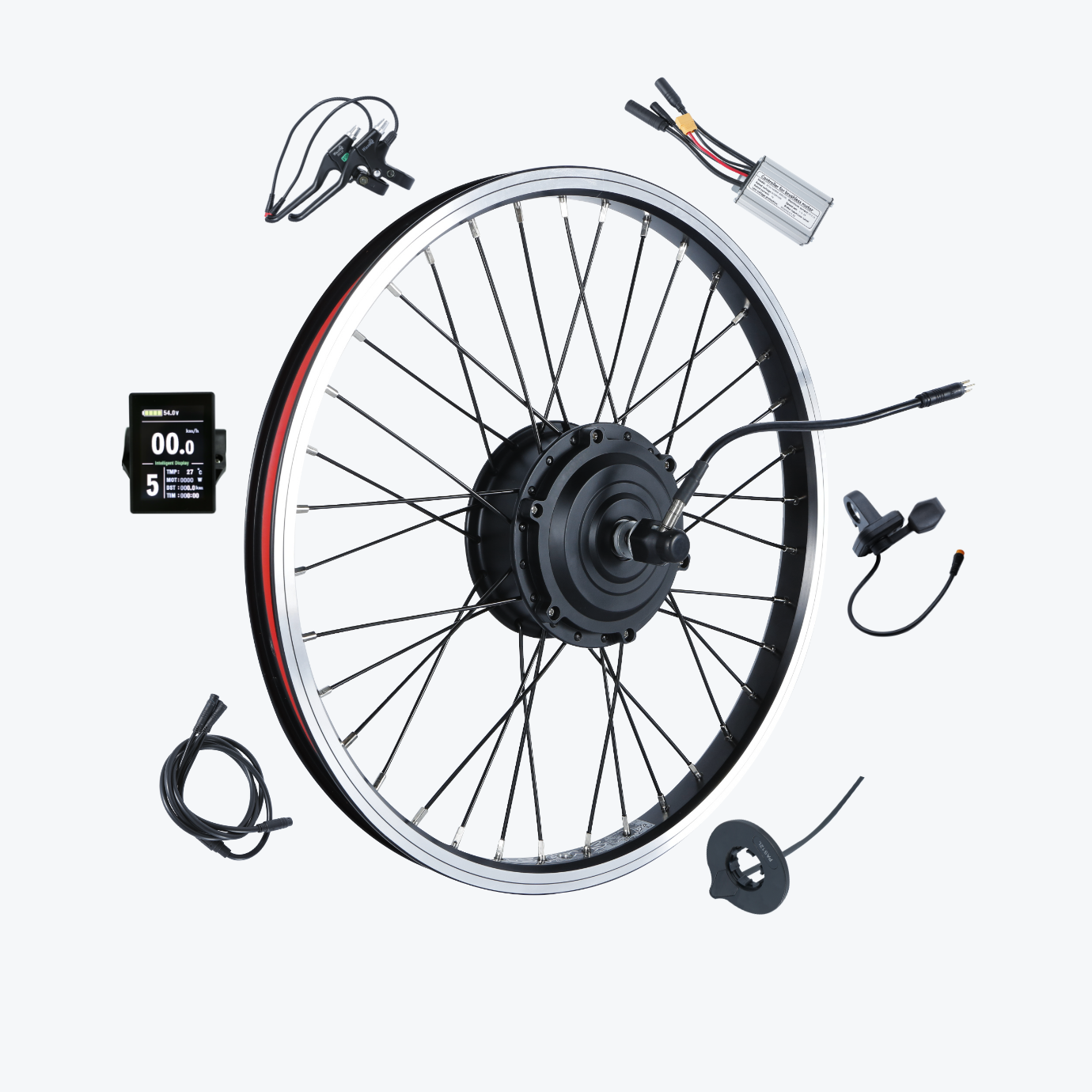
Converting your regular bike into an electric bike is easier than you might think. Whether you have a mountain bike collecting dust in your garage or a road bike you love but wish had a little more power, an e-bike conversion can breathe new life into your ride.
This comprehensive guide walks you through everything you need to know about transforming your conventional bicycle into an electric-powered machine, from choosing the right kit to completing the installation and enjoying your first electric ride.
Why Convert Your Bike to Electric?
Before diving into the how-to, let's explore why converting makes sense. The best ebike kit solutions offer several compelling advantages over buying a new e-bike:
Cost-Effective Solution
- Significantly cheaper than purchasing a complete e-bike
- Keep your existing bike frame and components you already love
- Upgrade only what's necessary for electric power
Customization Freedom
- Choose your preferred power level (250W to 4000W)
- Select battery capacity based on your riding needs
- Pick between hub motor or mid-drive systems
Environmental Benefits
- Reduce waste by repurposing your existing bicycle
- Avoid manufacturing impact of new e-bike production
- Lower carbon footprint compared to car transportation
Preserve Your Ride
- Keep the bike geometry and handling you're familiar with
- Maintain high-quality frame and components
- Retain emotional connection to your trusted bicycle
Choosing the Right Conversion Kit
Understanding Your Options
There are two main types of conversion systems available:
Hub Motor Kits
- Motor built into front or rear wheel
- Easier installation process (20 minutes typically)
- Available in power ranges from 250W to 4000W
- Suitable for most bike types and riding styles
Mid-Drive Motor Kits
- Motor mounts at bottom bracket (crank area)
- Superior hill-climbing performance with 140Nm torque
- Better weight distribution
- Works with existing bike gears for efficiency
Power Level Selection Guide
|
Power Output |
Best Applications |
Top Speed |
Range |
Ideal Bike Types |
|
250W-500W |
City commuting, legal compliance, flat terrain |
25-35 km/h |
40-70 km |
Road bikes, hybrids, folding bikes |
|
750W-1000W |
Hill climbing, daily commuting, moderate trails |
45-50 km/h |
35-60 km |
Hybrid, mountain bikes |
|
1500W-2000W |
Steep hills, fat tire bikes, performance riding |
50-60 km/h |
40-60 km |
Mountain bikes, fat bikes |
|
2500W-3000W |
Extreme terrain, high-performance applications |
75-85 km/h |
40-80 km |
MTB, fat tire bikes |
|
4000W |
Maximum power, extreme off-road, fat tire bikes |
75-85+ km/h |
40-80 km |
MTB, fat tire bikes |
Bike Compatibility Check
Before purchasing a conversion kit, verify your bike meets these requirements:
Frame Compatibility
- Sound frame structure without cracks or damage
- Steel, aluminum, or carbon frames all work (with proper torque arms)
- Adequate spacing in dropouts for motor axle
- Sufficient clearance for battery mounting
Wheel Size Options
- 16" (Brompton and compact folders)
- 20" (folding bikes, tricycles)
- 26" (mountain bikes, cruisers, fat bikes)
- 27.5" (modern mountain bikes)
- 28" (hybrid bikes)
- 29" (large mountain bikes)
- 700C (road bikes, touring bikes)
Brake System
- Disc brakes (mechanical or hydraulic)
- V-brakes or rim brakes
- Verify kit includes compatible brake sensors
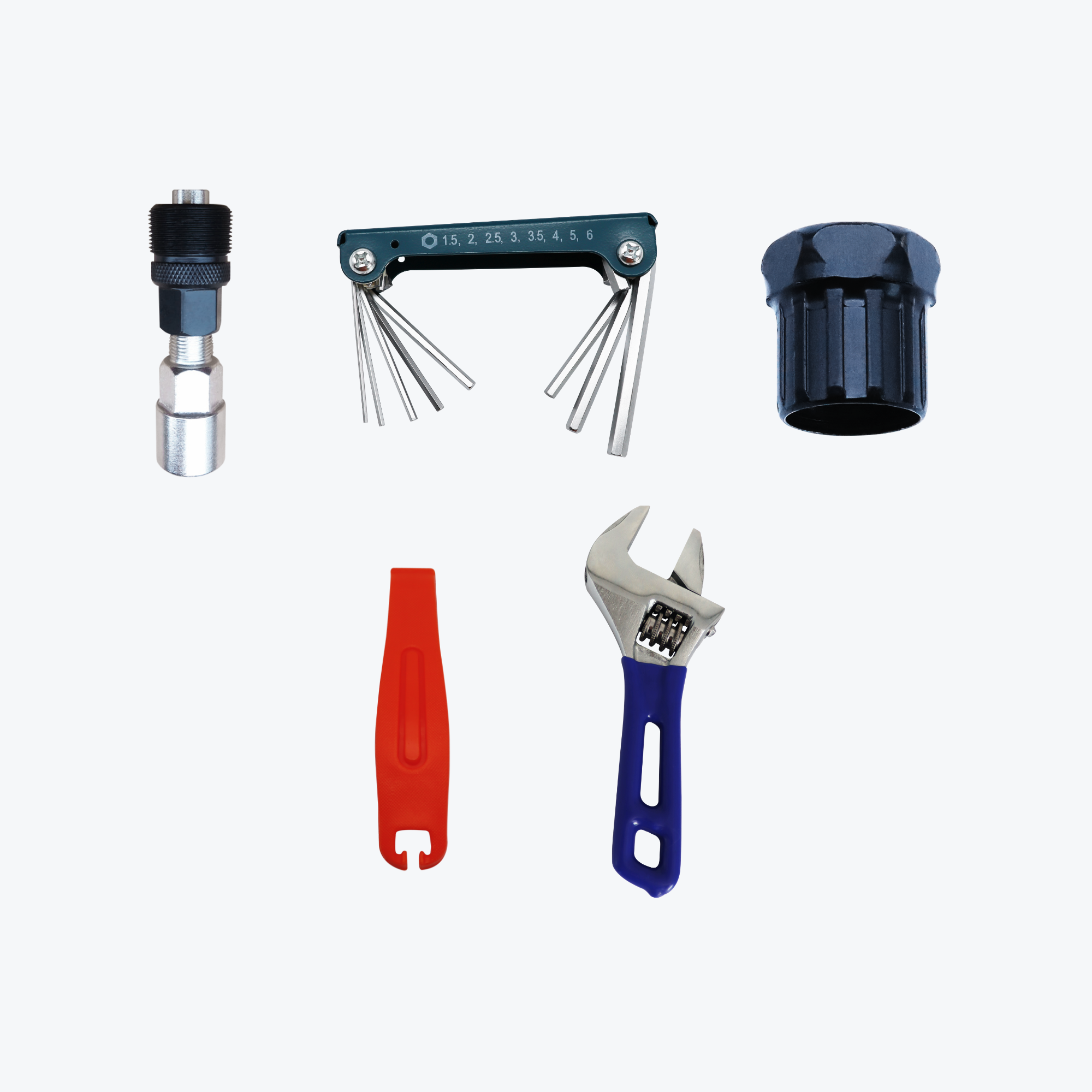
Required Tools and Materials

Essential Tools for Hub Motor Installation
- Allen key set (4mm, 5mm, 6mm most common)
- Adjustable wrench or 15mm pedal wrench
- Cassette removal tool (for rear wheel conversions)
- Chain whip (for rear wheel conversions)
- Tire levers
- Basic screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Cable ties for wire management
- Electrical tape
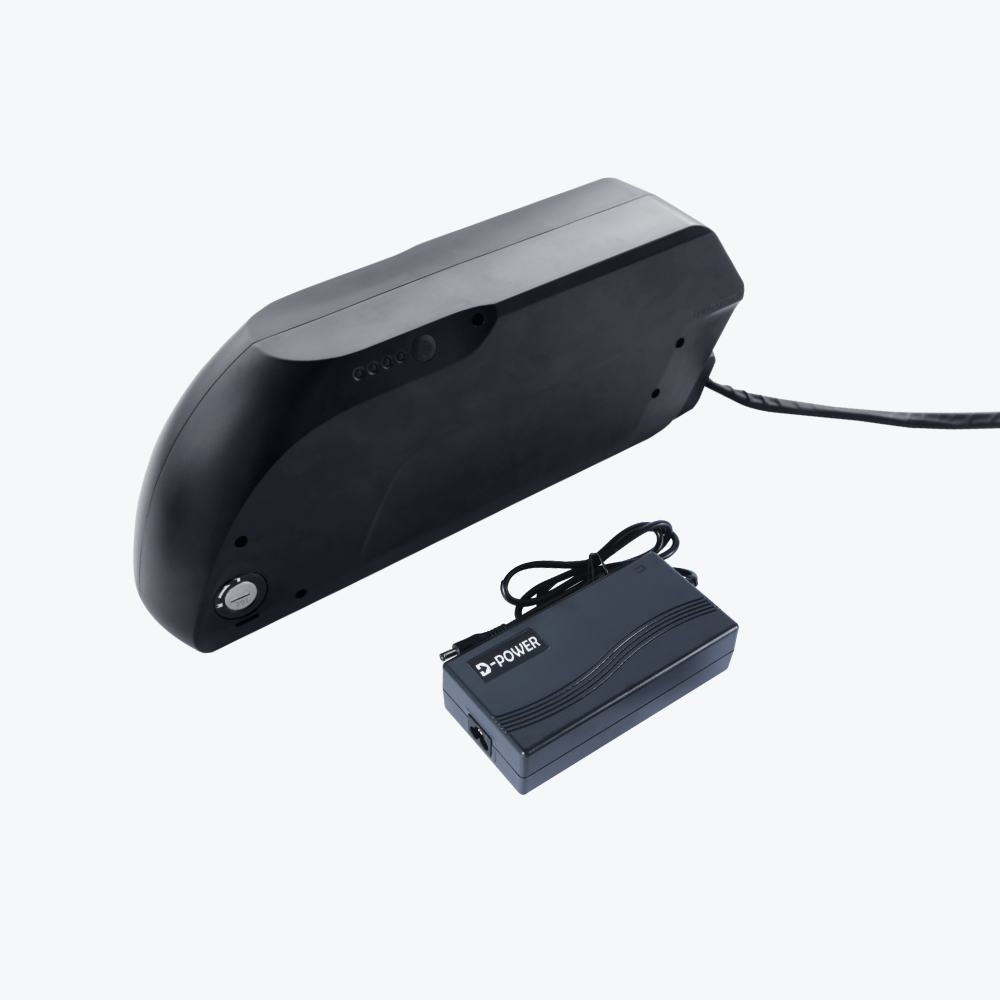
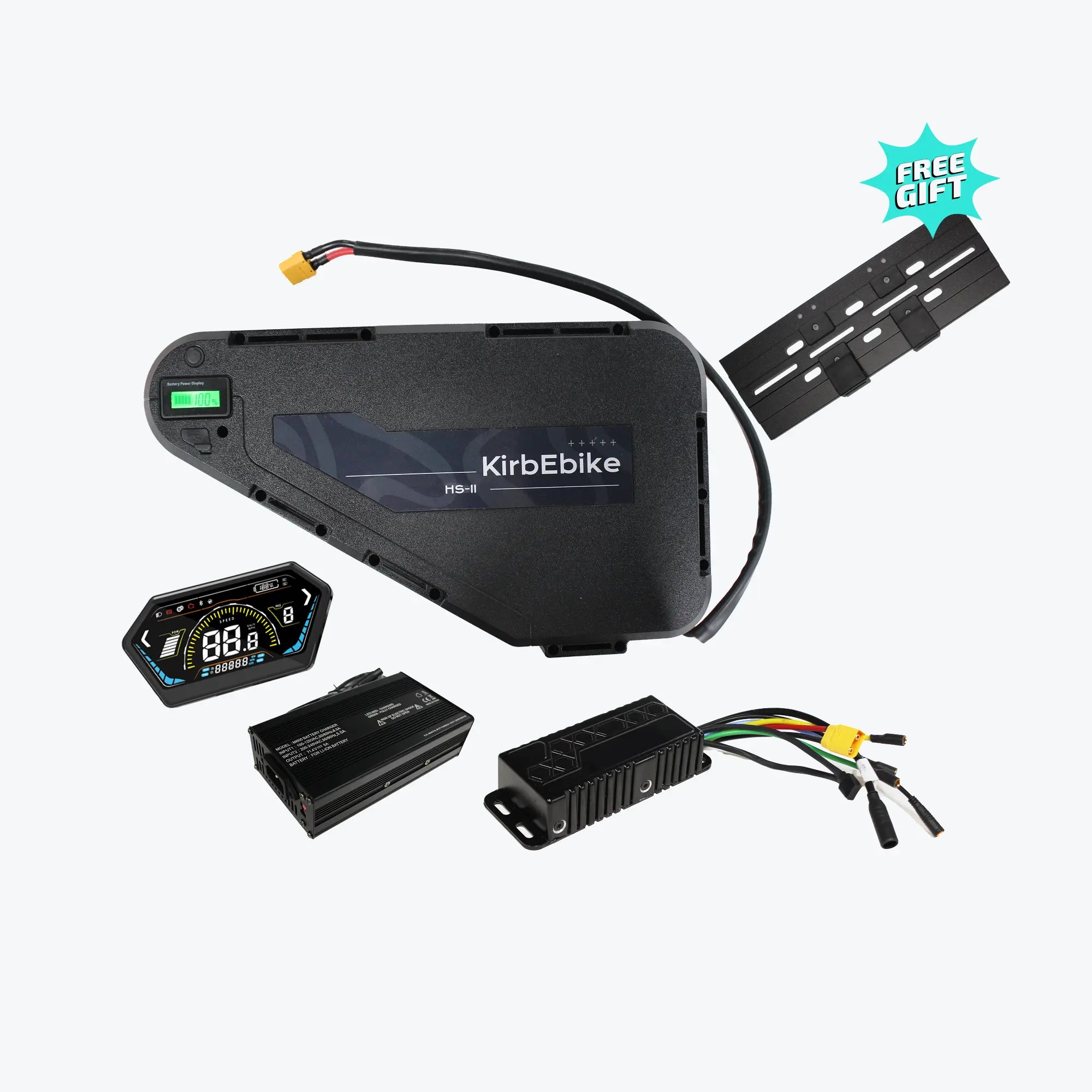
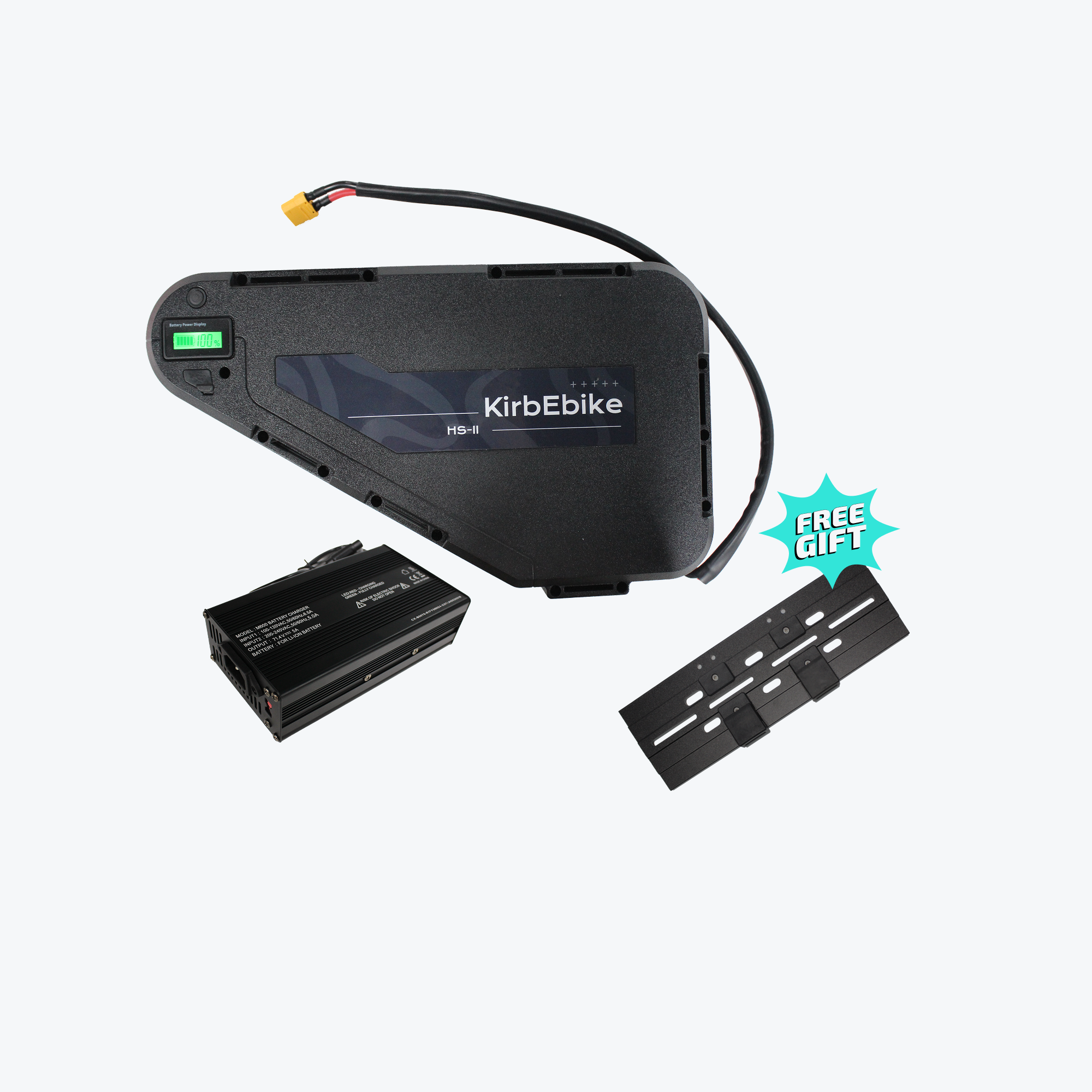
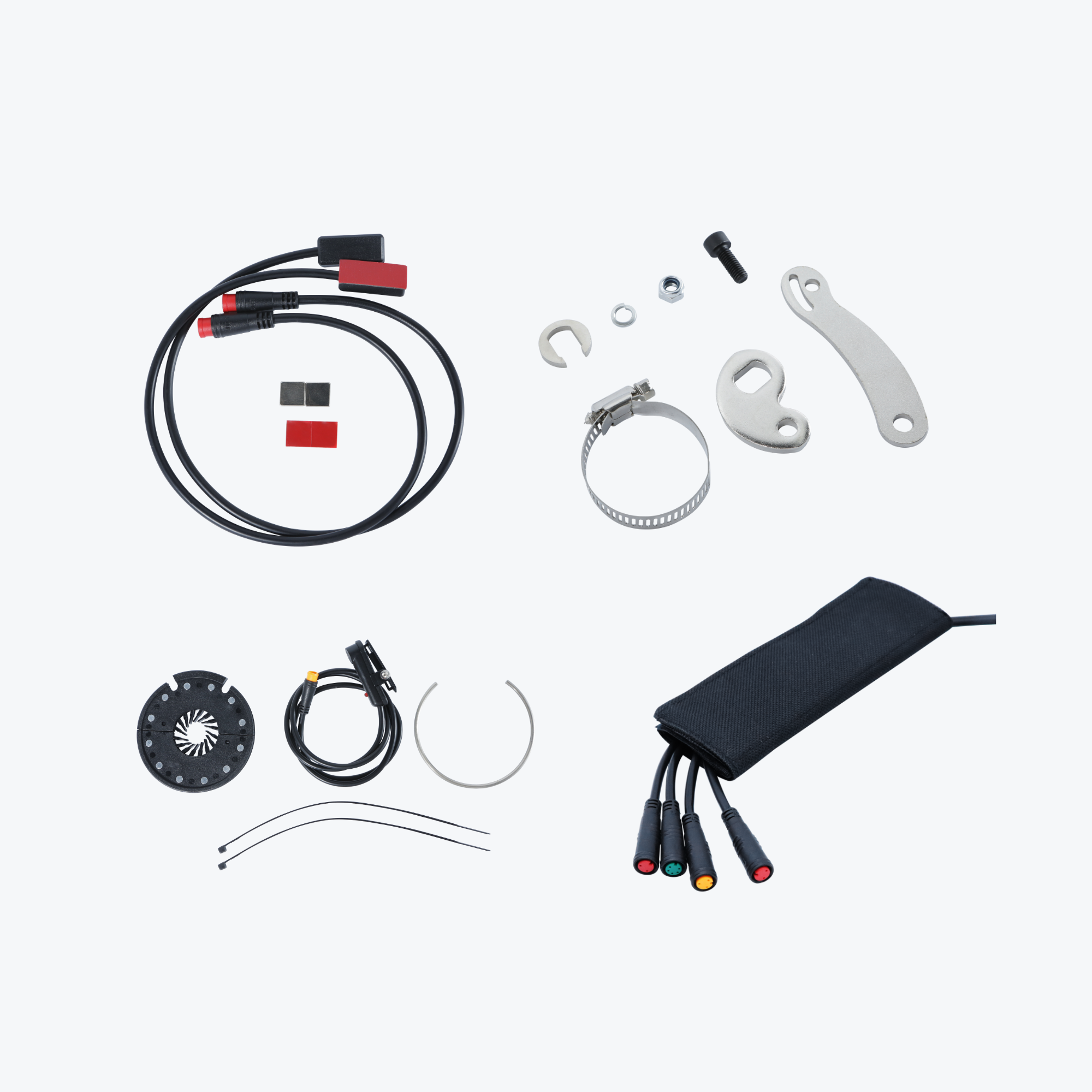
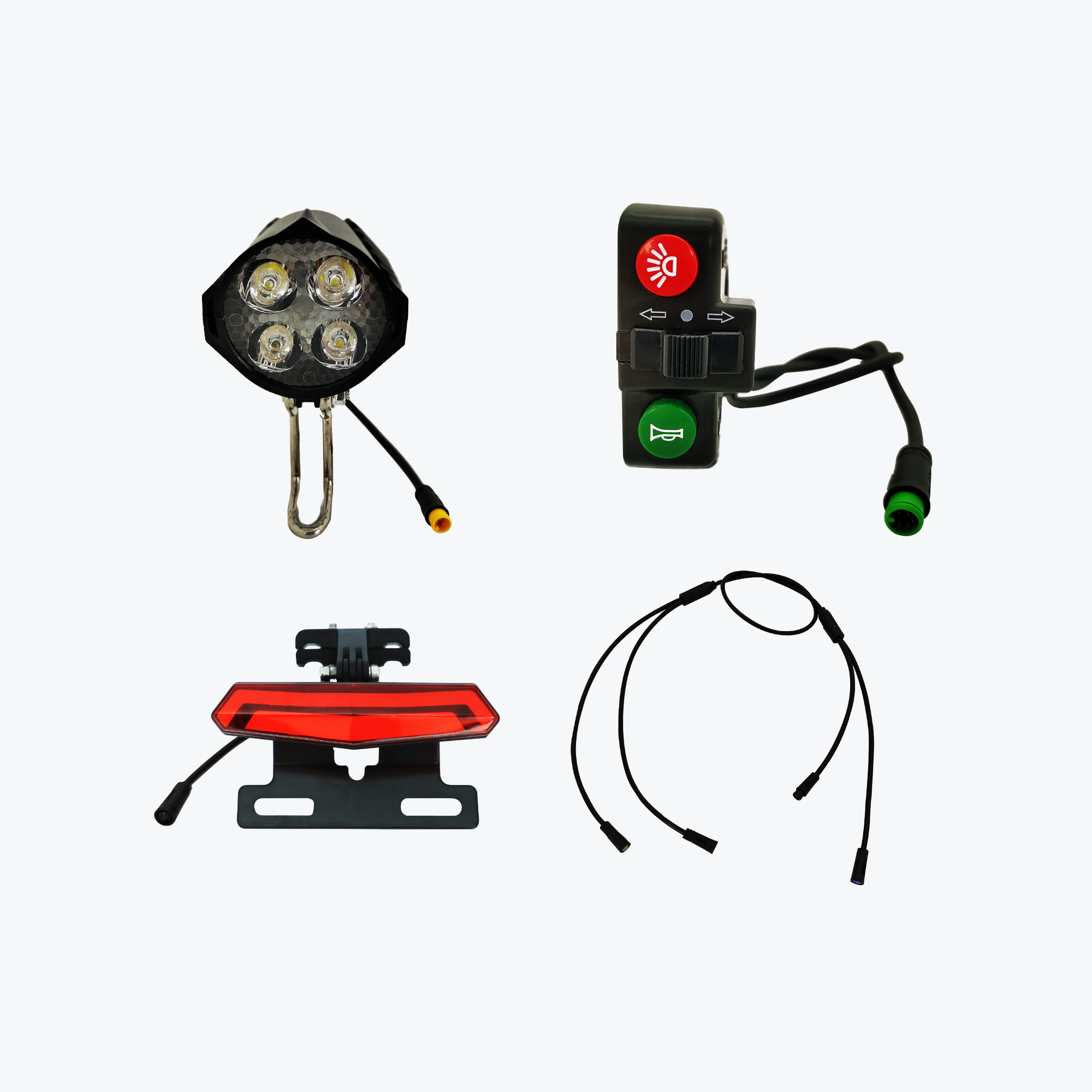
What's Included in Your Conversion Kit
A complete electric bike kit battery package contains:
Main Components
- Motor wheel (hub motor) or motor unit (mid-drive)
- Lithium battery pack with integrated locking system
- Battery charger (2A-5A depending on capacity)
- Controller (often pre-installed in motor or battery)
- LCD display unit with comprehensive ride data
Control Components
- Throttle (thumb or twist-grip style)
- Pedal assist sensor (cadence or torque type)
- Brake levers with motor cut-off switches
- All connecting cables and waterproof connectors
Installation Accessories
- Torque arms for frame protection
- Mounting brackets for battery
- Cable management clips
- Installation hardware (bolts, washers, spacers)
- Installation tools (cassette tool, pedal wrench)
- Detailed instruction manual
Step-by-Step Hub Motor Conversion

Phase 1: Preparation (5 minutes)
- Workspace Setup
- Choose clean, well-lit work area
- Place bike in repair stand if available
- Lay out all kit components for inventory check
- Have tools within easy reach
- Bike Preparation
- Clean bike thoroughly, especially dropout area
- Check frame for damage or cracks
- Verify brake operation before conversion
- Take photos for reference during reassembly
Phase 2: Wheel Removal and Transfer (10 minutes)
For Rear Wheel Conversions:
- Remove Existing Wheel
- Shift chain to smallest cog
- Release brake caliper or open quick-release
- Remove wheel from dropouts
- Set aside carefully with derailleur
- Transfer Components
- Remove tire using tire levers
- Extract inner tube
- Use cassette tool and chain whip to remove gears
- Remove disc brake rotor if equipped (6 bolts)
- Install on Motor Wheel
- Mount cassette onto motor wheel (hand-tight, then one click with tool)
- Install brake rotor with proper torque
- Mount tire ensuring directional arrows point forward
- Install new or existing inner tube
- Inflate tire to recommended pressure
For Front Wheel Conversions:
- Remove Front Wheel
- Release brake caliper or V-brake
- Loosen axle nuts or quick-release
- Remove wheel from fork dropouts
- Transfer Components
- Remove tire and tube
- Transfer to motor wheel
- Install brake rotor if disc brake equipped
- Inflate tire properly
Phase 3: Motor Wheel Installation (10 minutes)
- Install Motor Wheel
- Guide motor wheel into dropouts carefully
- Ensure motor cable exits on non-drive side
- Center wheel in frame/fork
- Tighten axle nuts securely (check manufacturer's torque specs)
- Install Torque Arms
- Critical for aluminum and carbon frames
- One torque arm minimum (two recommended for high power)
- Secure between frame and axle nuts
- Verify tight fit with no movement
- Adjust Brakes
- Reconnect brake caliper
- Adjust brake pads to new wheel alignment
- Test brake operation before proceeding
- Verify rotor doesn't rub
Phase 4: Battery Installation (5 minutes)
Down Tube Battery:
- Position mounting plate on down tube
- Mark bolt hole locations
- Install mounting bolts through existing bottle cage holes
- Slide battery onto mounting rails
- Lock battery with provided key
- Route power cable along frame to controller
Rear Rack Battery:
- Install rear rack if not present
- Secure battery mounting plate to rack
- Lock battery in position
- Route cables neatly along frame
Phase 5: Component Installation (10 minutes)
- Display Unit
- Remove existing handlebar grips if necessary
- Mount display bracket on handlebars
- Position for easy visibility while riding
- Secure with provided clamp
- Throttle Installation
- Choose right or left side based on preference
- Slide onto handlebar next to display
- Position comfortably for thumb access
- Tighten securely
- Brake Levers with Cut-Off Sensors
- Remove existing brake levers
- Install new levers with integrated sensors
- Connect to brake cables
- Adjust lever reach for comfort
- Test brake operation
- Pedal Assist Sensor
- Remove left-side crank bolt cap
- Slide sensor bracket onto bottom bracket
- Position sensor disc on crank arm
- Align sensor head with disc (2-3mm gap)
- Secure tightly
Phase 6: Electrical Connections (5 minutes)

Connection Sequence:
- Motor to Controller
- Thick 3-phase motor cable
- Waterproof connector (align and twist-lock)
- Ensure tight seal
- Battery to Controller
- Main power cable from battery
- Usually red/black thick wires
- Secure connection completely
- Display Connection
- Multi-pin connector to controller
- Match connector shape and pins
- Push firmly until click
- Sensor Connections
- Pedal assist sensor cable
- Brake sensor cables (left and right)
- Throttle connection
- Speed sensor if separate
- Cable Management
- Route all cables neatly along frame
- Use provided cable ties
- Avoid moving parts (crank, wheel)
- Prevent rubbing on tire or frame
- Leave slight slack for turning handlebars
Phase 7: System Testing (5 minutes)
- Pre-Ride Checks
- Verify all connections tight
- Check wheel rotates freely
- Test brakes cut motor power
- Confirm battery locked securely
- Inspect for any loose wires
- Power-Up Sequence
- Turn on battery (usually button press)
- Display should illuminate
- Check battery level indicator
- Verify speed reads zero
- Function Tests
- Lift rear wheel off ground
- Test throttlewheel should spin smoothly
- Activate brakemotor should cut immediately
- Test pedal assistmotor engages when pedaling
- Adjust assist level and verify response
- Final Adjustments
- Set preferred assist level
- Adjust display settings if available
- Configure speed limit if required
- Set wheel diameter for accurate speed reading
How to Convert a Mountain Bike to Electric

Mountain bikes make excellent conversion candidates due to their robust frames and wheel compatibility. Here's what makes MTB conversions special:
Optimal Kit Choices for Mountain Bikes:
- 48V 1000W Hub Motor: Perfect for trail riding and moderate hills
- 52V 2000W System: Excellent for aggressive trail riding and steep climbs
- Mid-Drive 500W-750W: Superior for technical terrain using existing gears
- 60V-72V High Power: Extreme off-road performance for experienced riders
MTB-Specific Considerations:
- Wheel Size Verification
- 26", 27.5", or 29" wheel size
- Check tire clearance with motor wheel
- Verify disc brake compatibility
- Frame Durability
- Most MTB frames handle conversion well
- Install dual torque arms for safety
- Check rear triangle stiffness
- Battery Mounting Options
- Down tube mounting most common
- Consider frame bag for protection
- Rear rack option reduces weight on suspension
- Suspension Compatibility
- Front wheel motor works with front suspension
- Rear motor works with rear suspension
- Mid-drive optimal for full-suspension bikes
Mid-Drive Motor Installation

The mid motor electric conversion kit installation differs significantly from hub motors:
Mid-Drive Installation Overview
Time Required: 30-40 minutes for experienced mechanics
Key Differences:
- Motor replaces bottom bracket instead of wheel
- Uses existing wheels and gears
- More complex but superior performance
- Requires bottom bracket removal tool
Installation Steps:
- Remove Existing Cranks
- Use crank puller tool
- Remove both pedals first
- Extract crank arms carefully
- Remove Bottom Bracket
- Use appropriate bottom bracket tool
- Remove cups from both sides
- Clean threads thoroughly
- Install Mid-Drive Unit
- Insert motor through bottom bracket shell
- Install mounting plates both sides
- Secure according to manufacturer specs
- Ensure motor sits flush and aligned
- Install Included Cranks
- Attach left and right crank arms
- Torque to proper specifications
- Install pedals with correct threading
- Connect Components
- Battery to controller
- Display and controls
- Torque sensor (pre-installed)
- Speed sensor on rear wheel
- Brake sensors
Mid-Drive Advantages:
- 140Nm maximum torque for hill climbing
- Better weight distribution (4.8kg motor weight)
- More natural pedaling feel
- Efficient use of bike gears
- Longer range through gear optimization
Battery Selection and Management
Choosing the right ebike kit battery significantly impacts your conversion success:
Battery Specifications Guide
|
Voltage |
Capacity |
Typical Range |
Best For |
Weight |
|
36V |
13-16Ah |
30-50 km |
Commuting, flat terrain |
2.5-3kg |
|
48V |
16-20Ah |
35-60 km |
General purpose, hills |
3-3.5kg |
|
52V |
20-30Ah |
40-70 km |
Extended range, performance |
3.5-4.5kg |
|
60V |
20Ah |
40-80 km |
High power applications |
4-5kg |
|
72V |
20Ah |
40-80 km |
Maximum performance |
4.5-5kg |
Battery Features to Consider
Cell Quality
- LG branded cells for reliability
- Samsung cells also high quality
- Avoid generic cell manufacturers
- Check for genuine certification
Battery Management System (BMS)
- Overcharge protection essential
- Short circuit protection
- Temperature monitoring
- Cell balancing for longevity
- 60Amp discharge capability for high power
Physical Features
- Integrated locking mechanism
- Waterproof construction (IP rating)
- LED charge level indicator
- Easy removal for charging
- Durable aluminum housing
Charging Specifications
- 2A charger for smaller batteries (8-10 hours)
- 5A fast charger for large batteries (4-6 hours)
- 1000+ charge cycle lifespan
- Smart charging with auto-shutoff
Testing and First Ride
Pre-Ride Safety Checklist
Before your first electric ride, verify:
- All bolts tightened to proper torque
- Motor wheel spins freely without rubbing
- Brakes function properly and cut motor power
- Battery fully charged and locked
- Display shows correct information
- Throttle responds smoothly
- Pedal assist engages properly
- No loose wires or cables
- Tire pressure correct
- All connections waterproof and secure
First Ride Protocol
- Start in Safe Area
- Empty parking lot or quiet street
- Flat, smooth surface preferred
- Away from traffic initially
- Begin with Low Assist
- Start at assist level 1 or 2
- Get feel for motor engagement
- Practice smooth starts
- Test All Functions
- Try throttle-only operation
- Test each pedal assist level
- Verify brake cut-offs work
- Check different speeds
- Gradual Progression
- Increase power gradually
- Test hill climbing ability
- Verify battery range estimates
- Get comfortable with weight and handling
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Motor Not Starting
Possible Causes and Solutions:
- Battery Issues
- Check battery charge level
- Verify battery turned on
- Inspect main power connection
- Try different battery if available
- Connection Problems
- Check all connector pins
- Verify waterproof seals intact
- Look for loose or corroded connections
- Test continuity with multimeter
- Brake Sensor Activation
- Brake sensors may be stuck "on"
- Adjust sensor position
- Check sensor magnet alignment
- Disconnect to test if sensor faulty
Limited Range or Power
Diagnosis Steps:
- Battery Health
- Check actual voltage (should match rating)
- Verify charge cycles (degrades over time)
- Test under load
- Consider replacement if old
- System Settings
- Verify correct wheel diameter programmed
- Check speed limit settings
- Confirm proper voltage setting
- Reset controller if needed
- Mechanical Issues
- Check tire pressure (low pressure drains battery)
- Verify no brake drag
- Inspect for bearing wear
- Ensure chain properly lubricated
Display Errors
Common Error Codes:
- Error 21: Controller issue
- Error 22: Throttle problem
- Error 23: Motor phase issue
- Error 24: Speed sensor problem
- Error 30: Communication error
Resolution:
- Power cycle entire system
- Check specific component mentioned
- Verify all connections tight
- Consult manufacturer documentation
- Contact technical support if persistent
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to convert a bike to electric?
Most hub motor conversions take just 20 minutes with basic tools. Mid-drive installations require 30-40 minutes. First-time converters should allow extra time to familiarize themselves with components and ensure all connections are secure.
Can any bike be converted to electric?
Yes, nearly any bike with a sound frame can be converted. Kits are available for all wheel sizes from 16" to 29" and 700C, fitting mountain bikes, road bikes, hybrids, folding bikes, and even tricycles. Verify your frame has no cracks and adequate clearance for battery mounting.
Do I need special tools for the conversion?
No special tools required for hub motor kits basic Allen keys, wrenches, and a cassette tool (included) are sufficient. Mid-drive conversions need a bottom bracket removal tool. Most kits include essential installation tools, and you likely already own the necessary items.
How much range can I expect after conversion?
Range varies by battery capacity and power level: 30-50km with 36V systems, 35-60km with 48V, and 40-80km with 52V-72V batteries. Factors affecting range include rider weight, terrain, assist level, tire pressure, and weather conditions.
Will converting my bike void its warranty?
Most bike warranties don't cover modifications, so conversion may void the original warranty. However, conversion kits come with their own 1-year warranty covering motor, battery, and electronic components. Keep your original parts if warranty concerns exist.
Conclusion
Converting your regular bike to electric opens up new possibilities for commuting, recreation, and adventure. Whether you choose a simple hub motor setup or a sophisticated mid-drive system, the transformation process is straightforward and rewarding.
With proper installation, quality components from the electric bike kit battery range, and regular maintenance, your converted e-bike will provide years of reliable, enjoyable service.The 20-minute installation for hub motors or 30-40 minutes for mid-drive systems represents a small investment of time for significant long-term benefits.
You'll preserve your favorite bike while gaining electric assistance, save considerable expense compared to buying new, and join the growing community of e-bike enthusiasts making sustainable transportation choices.Ready to start your conversion journey? Explore the complete range of conversion kits and accessories to find the perfect match for your bike and riding style.