Are you looking for a way to upgrade your bike with an electric motor? If so, you may have heard of two types of motors that are commonly used for e-bikes: rear hub motor and mid-drive motor. But what are they and how do they work? And more importantly, which one is better for e-bikes?
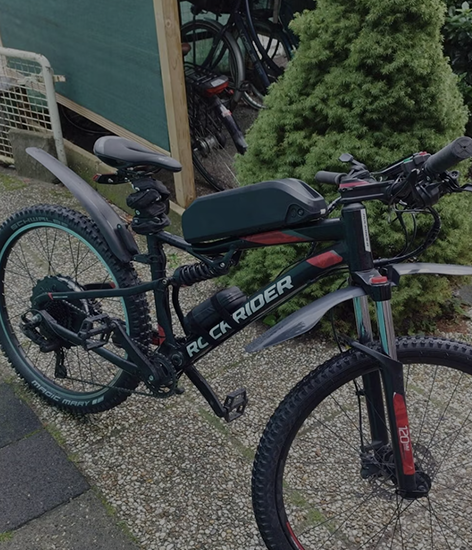
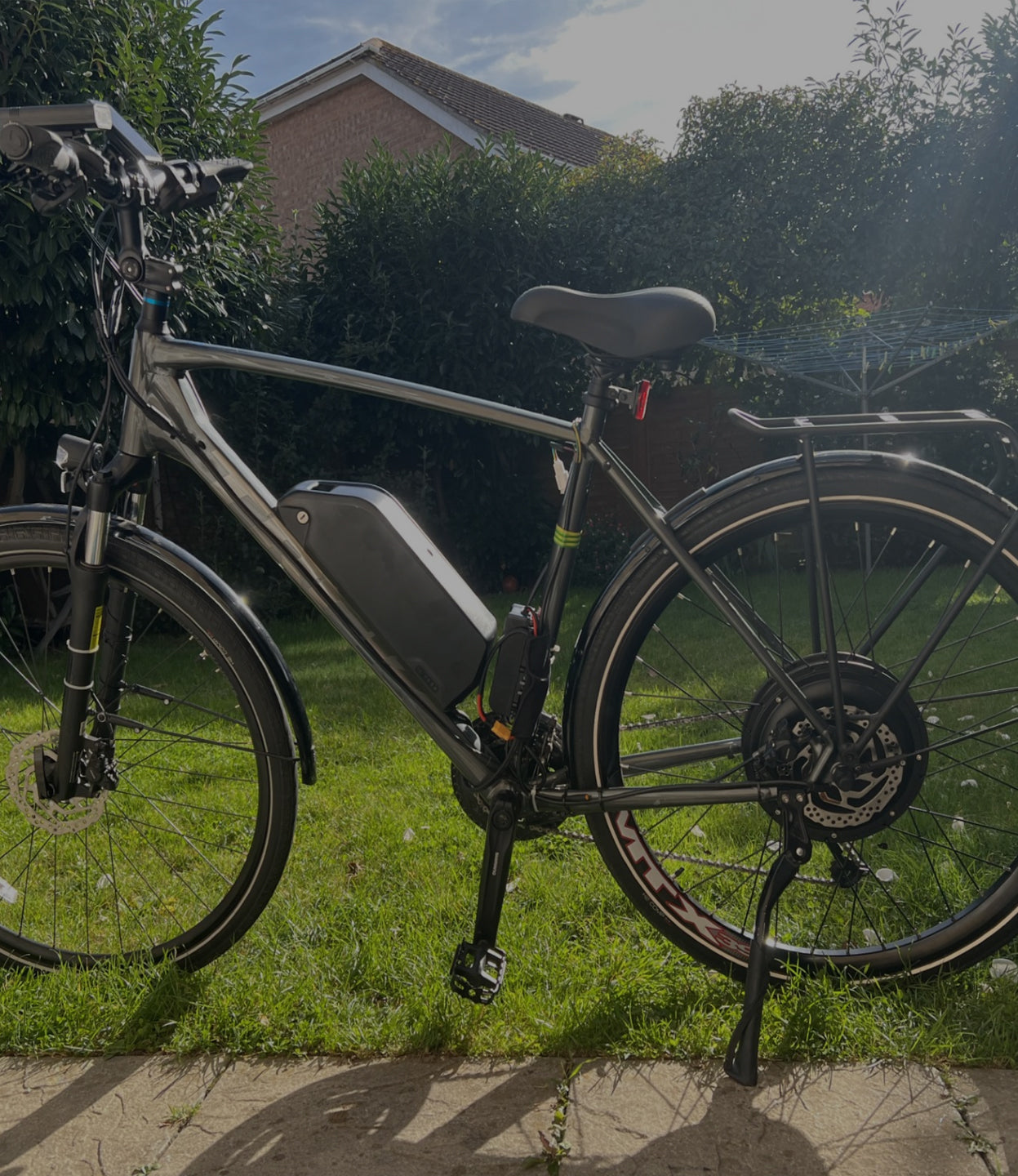
A rear hub motor ebike features a motor that is mounted on the rear wheel, spinning the wheel directly without using the bike's chain or gears. In contrast, a mid-drive motor, also known as a mid drive vs hub motor, is mounted on the bottom bracket of the bike and utilizes the bike's chain and gears to power the rear wheel.
Both types of motors have their advantages and disadvantages, depending on your riding style, preferences, and budget. In this article, we will compare them based on five criteria: performance, efficiency, durability, cost, and maintenance. By the end of this article, you will have a better idea of which one is more suitable for your e-bike project. Let's get started!
Performance: How Rear Hub Motor and Mid-Drive Motor Affect Your Riding Feel, Speed, Torque, and Gear Ratio

Electric bike buyers often compare mid drive vs hub motor systems. The main difference between these hub drive motor options is how they power the bike. Rear hub motors spin the wheel directly, while mid-drive motors use the bike's chain and gears. This difference affects the bike's riding feel, speed, torque, and gear ratio.
Hub drive motors, such as rear hub motors, are simpler and have a smoother power delivery, regardless of pedaling cadence or terrain. They also have a higher top speed than mid-drive motors. However, rear hub motors have lower torque and less hill-climbing ability.
Mid-drive motors , in the hub motor vs mid drive efficiency debate, are more complex and offer a more dynamic power delivery, depending on pedaling cadence, terrain, and gear selection. They have lower top speed than rear hub motors, but higher torque and more hill-climbing ability.
Which type of motor is right for you depends on your riding style and preferences. If you ride fast on flat roads or downhill trails, a rear hub motor may be a good choice for its higher speed and smoother feel. If you ride on steep hills or off-road trails, a mid-drive motor may be a better choice for its higher torque and more dynamic feel.
Here are some specific examples of how the two types of motors affect different performance factors:
- Riding feel: Rear hub motors have a more "assisted" feel, while mid-drive motors have a more "natural" feel. This is because mid-drive motors use the bike's gears, which gives you more control over the power delivery.
- Speed: Hub motors, particularly rear hub motors, generally have a higher top speed than mid-drive motors. This is because they are not limited by the bike's gear range.
- Torque: Mid-drive motors have higher torque than rear hub motors. This makes them better for climbing hills and carrying heavy loads.
- Gear ratio: Rear hub motors are not limited by the bike's gear range, so you can use them with any gear ratio. Mid-drive motors are limited by the bike's gear range, but they still offer a wide range of gears to choose from.
Decoding Efficiency: How Rear Hub vs Mid-Drive Motors Use Battery Power

When choosing an ebike, efficiency matters. An efficient motor converts battery power into optimal performance while minimizing wasted energy. This impacts battery life and riding range.
Overall, mid-drive motors are more efficient than rear hubs. Here's why:
- Rear hubs directly spin the wheel, without using gears. This generates more heat and friction, draining the battery faster.
- Mid-drives utilize gearing. By optimizing torque at lower speeds, they conserve battery power. Less waste means longer range.
- Rear hubs work harder climbing hills, rapidly sapping battery power. Mid-drives use gears to match resistance, preserving juice.
- Rear hubs excel at flat terrain. But mid-drives maintain efficiency across conditions.
Consider your riding style when choosing between motor types. If you ride far or tackle lots of hills, a mid-drive's efficiency extends range. For shorter, flatter rides, a rear hub suffices.

Comparing Durability: Rear Hub Motors vs. Mid-Drive Motors Under Varying Conditions
When it comes to the durability of e-bike motors, one must consider how well they can resist the onslaught of wear and tear as well as environmental factors. Generally, rear hub motors tend to be more durable than mid-drive motors due to their simpler design and the reduced stress they place on the drivetrain.
Rear hub motors are typically more durable because they possess fewer moving parts, which decreases the likelihood of mechanical failure. They're also designed to ensure less strain on the drivetrain, further enhancing their longevity.
Additionally, rear hub motors display remarkable resilience when faced with challenging riding conditions, such as rough or wet terrains. This is because they are effectively sealed, offering robust protection against water, dust, and other potentially damaging debris.
Conversely, mid-drive motors, while offering certain performance advantages, tend to be slightly less durable than their rear hub counterparts. They have more moving parts, which inherently increases the risk of mechanical breakdowns.
Additionally, the added stress they put on the drivetrain can potentially lead to more frequent maintenance or repairs. When exposed to harsh or wet conditions, mid-drive motors can be more vulnerable since they are less shielded from environmental elements like water, dust, and debris.
Your riding conditions and preferences play a crucial role in determining the best motor choice for you. If you primarily ride on smooth, dry roads or trails, a mid-drive motor might be your best bet due to its superior efficiency and performance. However, if you frequently traverse rough or damp terrains, you might find a rear hub motor more suitable due to its enhanced durability and reliability.
Cost: How Rear Hub Motor and Mid-Drive Motor Differ in Price and Value
One of the factors that you need to consider when choosing a motor for your e-bike is the cost. The cost includes both the initial purchase price and the installation fee of the motor. Generally, rear hub motors are cheaper and easier to install than mid-drive motors, which means that you can save money and time with them.
Rear Hub Motors:
- Cost-Effective: Rear hub motors are more affordable due to their simpler design that uses standard parts and components. This simplicity lessens the production and shipping costs, making rear hub motors a cost-effective choice. The price range for various brands and models typically falls between $100 to $500.
- Easy Installation: One of the advantages of rear hub motors is their ease of installation. They don't require any modifications to your bike's frame, chain, or gears. The installation process involves swapping your original rear wheel with the motorized one and connecting it to the battery and controller. This can be done by yourself or with the help of a professional for a nominal fee.
Mid-Drive Motors:
- Higher Cost: Mid-drive motors tend to be more expensive due to their more complex design that uses customized parts and components. This complexity increases both the production and shipping costs. The price range for mid-drive motors from different brands and models is usually between $300 to $800.
- Installation Requires Expertise: Installing mid-drive motors tends to be more challenging as it requires some modifications to your bike's frame, chain, or gears. The installation process involves removing your original bottom bracket and crankset and replacing them with the motorized ones. Then, they need to be connected to the battery and controller. Due to the complexity involved, you might need to hire a professional for this task, which could come at a higher fee.
Depending on your budget and preferences, you may prefer one type of motor over the other. For example, if you have a tight budget or want a simple DIY project, you may prefer a rear hub motor for its lower cost and easier installation. On the other hand, if you have a flexible budget or want a professional service, you may prefer a mid-drive motor for its higher quality and performance.
Maintenance: How Rear Hub Motor and Mid-Drive Motor Require Different Levels of Care and Repair
The final criterion to compare rear hub motor and mid-drive motor is their maintenance. Maintenance refers to how much care and repair the motor requires to keep it in good condition and extend its lifespan. Generally speaking, rear hub motors have a lower maintenance than mid-drive motors, because they have fewer components and less wear and tear.
Rear hub motors have a lower maintenance than mid-drive motors because they have fewer components and less wear and tear. This means that they have less risk of malfunctioning or breaking down due to mechanical issues. Rear hub motors also have a lower maintenance when riding on rough or wet terrains, because they are sealed and protected from water, dust, and debris. You just need to check the tire pressure, the brake pads, and the spokes regularly.
Mid-drive motors have a higher maintenance than rear hub motors because they have more components and more wear and tear. This means that they have more risk of malfunctioning or breaking down due to mechanical issues. Mid-drive motors also have a higher maintenance when riding on rough or wet terrains, because they are exposed and vulnerable to water, dust, and debris. You need to check the chain, the gears, the bottom bracket, and the motor regularly.
Depending on your preferences and skills, you may prefer one type of motor over the other. For example, if you want a hassle-free and low-cost e-bike, you may prefer a rear hub motor for its lower maintenance and simpler design. On the other hand, if you want a high-performance and customizable e-bike, you may prefer a mid-drive motor for its higher maintenance and complex design.
Conclusion
In this article, we have compared rear hub motor and mid-drive motor, two types of motors that are commonly used for e-bikes. We have evaluated them based on five criteria: performance, efficiency, durability, cost, and maintenance. We have also provided you with some examples, references, and tips to help you make an informed decision.
So, which one is better for e-bikes? The answer depends on your personal preferences, budget, and riding style. There is no definitive answer, as each type of motor has its pros and cons. However, here are some general guidelines that may help you choose:
- If you want a simple, smooth, and fast e-bike, you may prefer a rear hub motor for its higher speed, lower cost, and easier installation.
- If you want a complex, dynamic, and powerful e-bike, you may prefer a mid-drive motor for its higher torque, higher efficiency, and more responsiveness.
We hope that this article has helped you understand the differences between rear hub motor and mid-drive motor and how they affect your e-bike experience. We also hope that you have enjoyed reading this article and learned something new from it. Thank you for your time and attention. Happy riding!

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main difference between rear hub motors and mid-drive motors?
Rear hub motors are attached to the rear wheel of the e-bike and power it directly. Mid-drive motors are attached to the frame of the e-bike and power the cranks.
Which motor is better for hilly terrains?
Mid-drive motors are better for hilly terrains because they have higher torque. This means that they can help you climb hills more easily. Rear hub motors also have torque, but not as much as mid-drive motors.
Are mid-drive motors suitable for daily commuting?
Yes, mid-drive motors are suitable for daily commuting. They are efficient and responsive, making them ideal for city riding. However, they can be more expensive than rear hub motors.
Do rear hub motors require less maintenance?
Yes, rear hub motors generally require less maintenance than mid-drive motors. This is because they have fewer moving parts.
What is the average lifespan of these motors?
The average lifespan of both rear hub motors and mid-drive motors is around 5 years. However, this can vary depending on the quality of the motor, how often you ride your e-bike, and how well you maintain it.
How do these motors impact the overall weight of the e-bike?
Mid-drive motors are generally heavier than rear hub motors. This is because they have more moving parts. However, the weight difference is usually not significant.
Can I retrofit my existing bike with either motor type?
Yes, you can retrofit your existing bike with either a rear hub motor or a mid-drive motor. However, it is important to choose a kit that is compatible with your bike frame and drivetrain.
What is the future of e-bike motor technology?
E-bike motor technology is constantly evolving. Newer motors are becoming more efficient, lighter, and more powerful. We can also expect to see more innovative motor designs in the future.