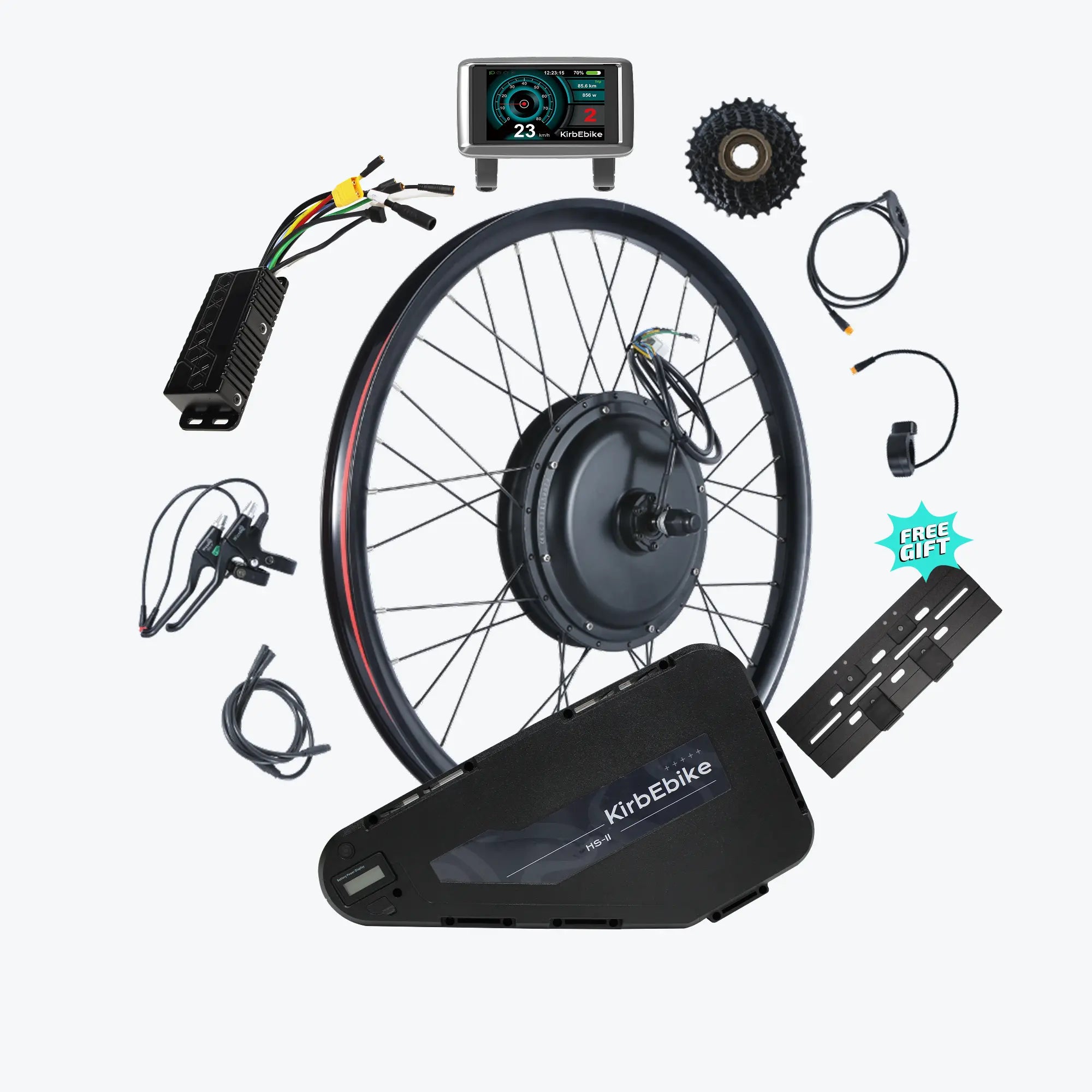
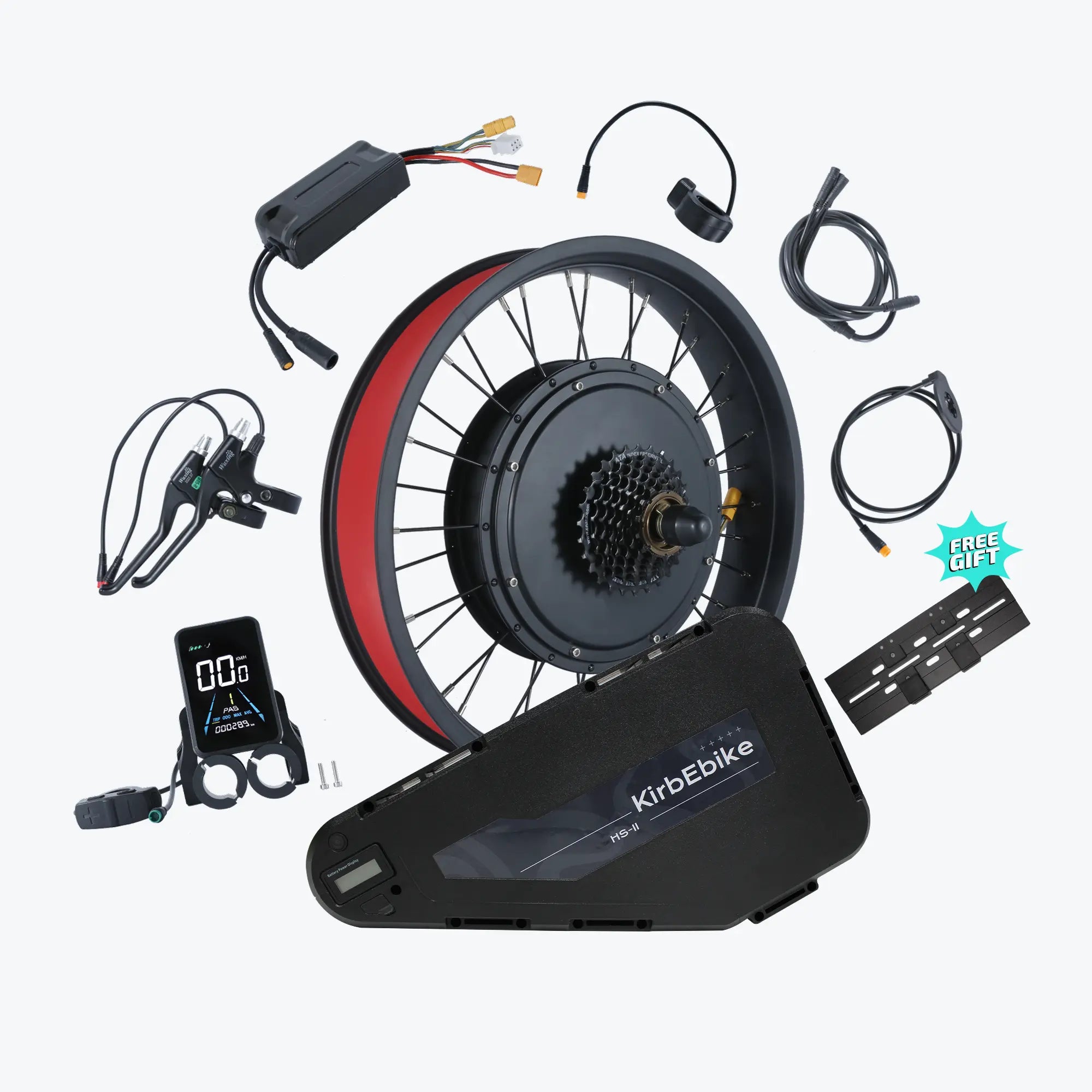
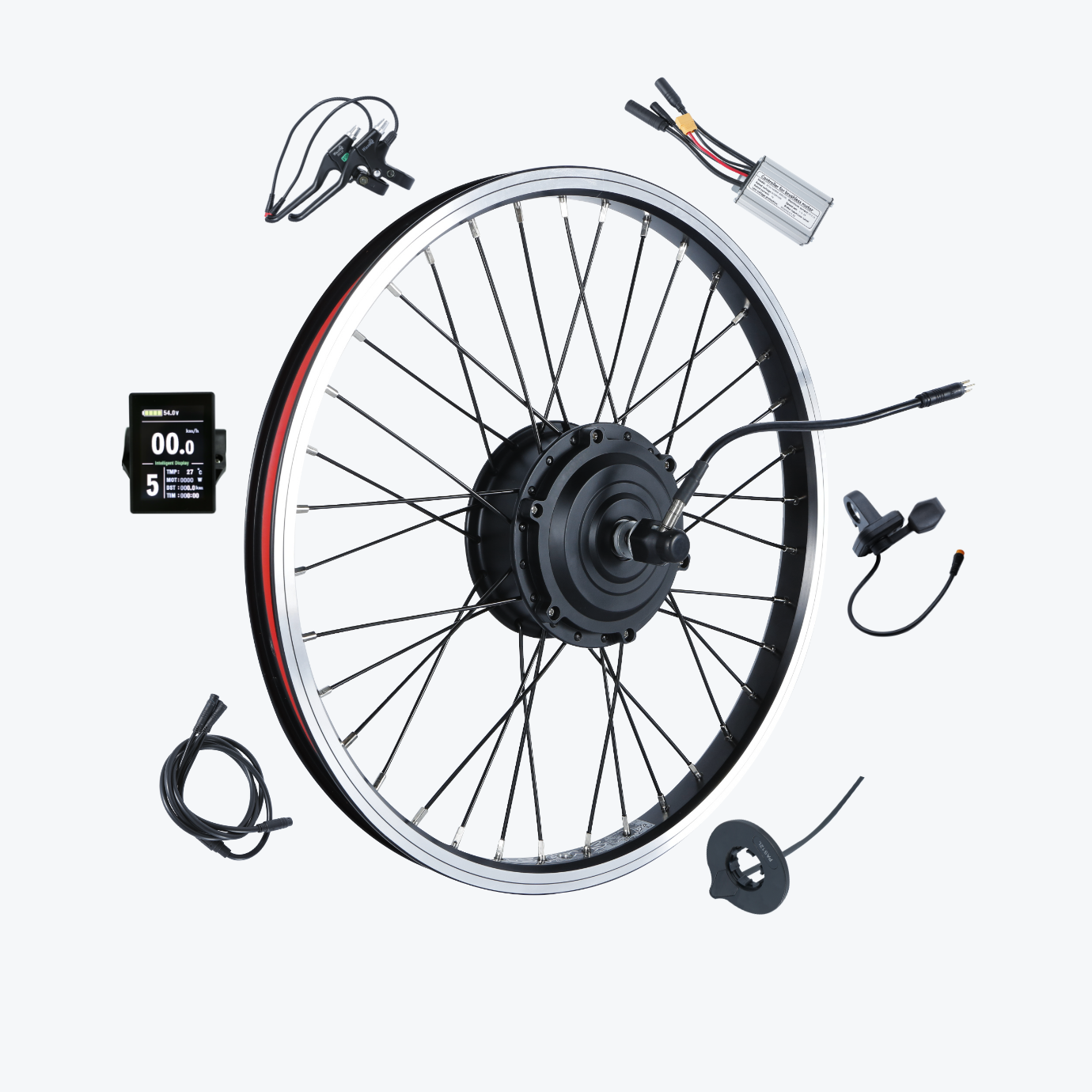
Installing an e-bike conversion kit transforms your regular bicycle into an electric-powered machine in just 20-40 minutes—but only if you avoid common installation errors that can compromise safety, performance, and component longevity.
While modern conversion kits from reputable manufacturers are designed for straightforward DIY installation, first-time installers frequently make preventable mistakes that lead to poor performance, premature wear, or even dangerous failures.
This comprehensive guide identifies the most critical installation errors and provides proven solutions to ensure your conversion succeeds perfectly the first time.
Understanding Installation Success
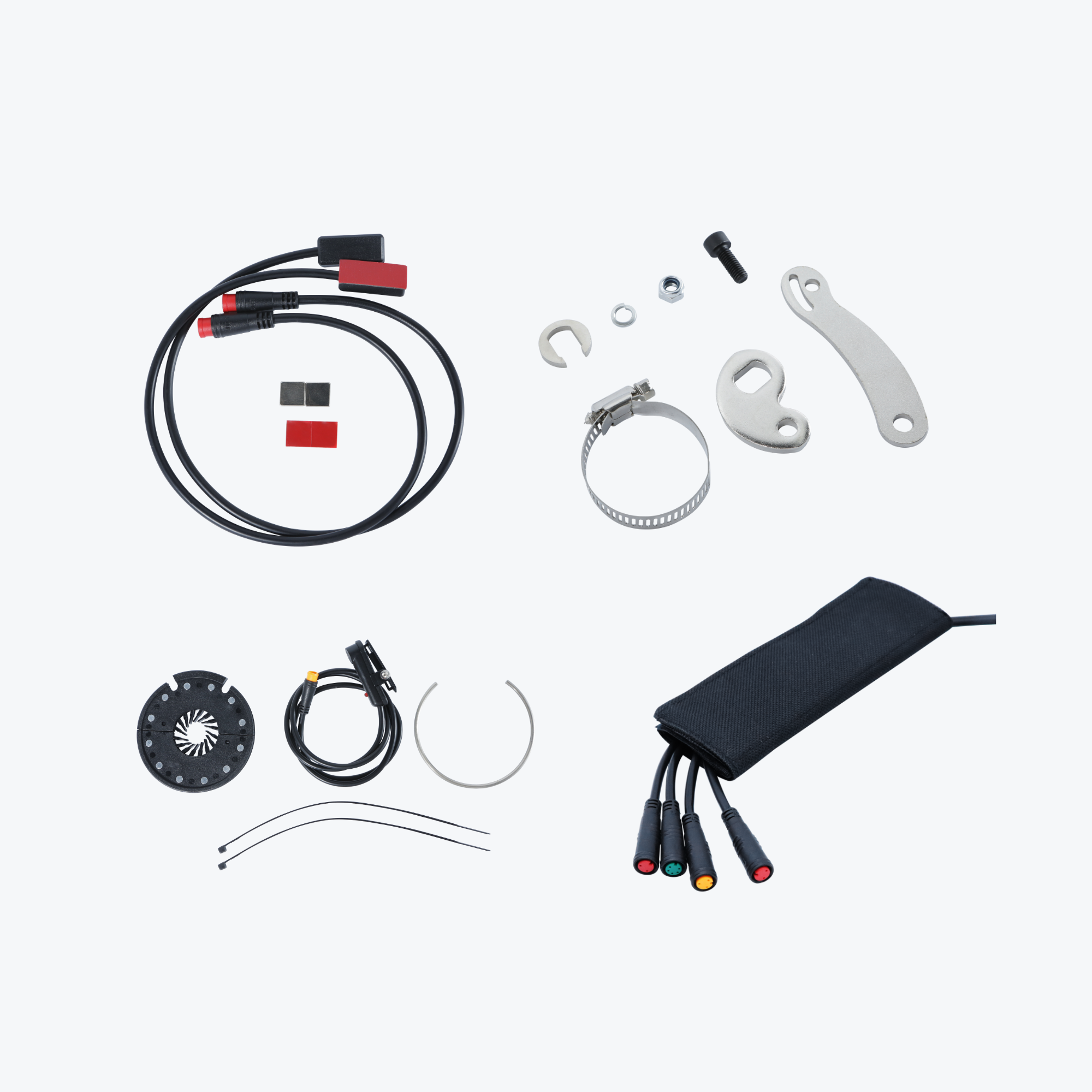
The best ebike kit systems include everything needed for successful installation: motor, battery, controller, display, sensors, hardware, tools, and comprehensive instructions. However, installation success depends equally on following proper procedures and avoiding common pitfalls that compromise the system.
Why Installation Quality Matters
Critical Pre-Installation Mistakes
Mistake #1: Not Reading Instructions Completely
The Error: Many installers jump straight to physical installation without thoroughly reviewing all documentation, videos, and resources provided.
Why It's Problematic:
- Miss critical preparation steps
- Overlook compatibility warnings
- Skip essential safety procedures
- Waste time backtracking
- Risk component damage
The Solution:
Before touching any components:
- Watch entire installation video start to finish
- Read complete instruction manual
- Review all included documentation
- Check manufacturer's website for updates
- Join online community for tips
Preparation Checklist:
- ✓ Understand complete process flow
- ✓ Identify all components and their functions
- ✓ Note any bike-specific considerations
- ✓ Gather all required tools
- ✓ Prepare adequate workspace
- ✓ Allow sufficient time without rushing
Mistake #2: Inadequate Workspace Preparation
The Error: Beginning installation in cramped, poorly lit, or unsuitable locations without proper organization.
Problems Created:
- Lost small components
- Difficulty accessing bike areas
- Poor visibility for connections
- Frustration and errors
- Extended installation time
The Solution:
Ideal Workspace Setup:
- Clean, well-lit area with adequate space
- Bike repair stand or secure mounting
- Flat surface for organizing components
- Good lighting from multiple angles
- All tools within easy reach
- Component trays or containers for small parts
Organization Strategy:
- Lay out all kit components systematically
- Verify everything against packing list
- Group related components together
- Keep fasteners organized by type
- Have camera ready for documentation
Mistake #3: Wrong Tool Selection
The Error: Attempting installation with inappropriate, low-quality, or incorrectly sized tools.
Consequences:
- Stripped fasteners
- Damaged components
- Rounded bolt heads
- Improper torque application
- Personal injury risk
The Solution:
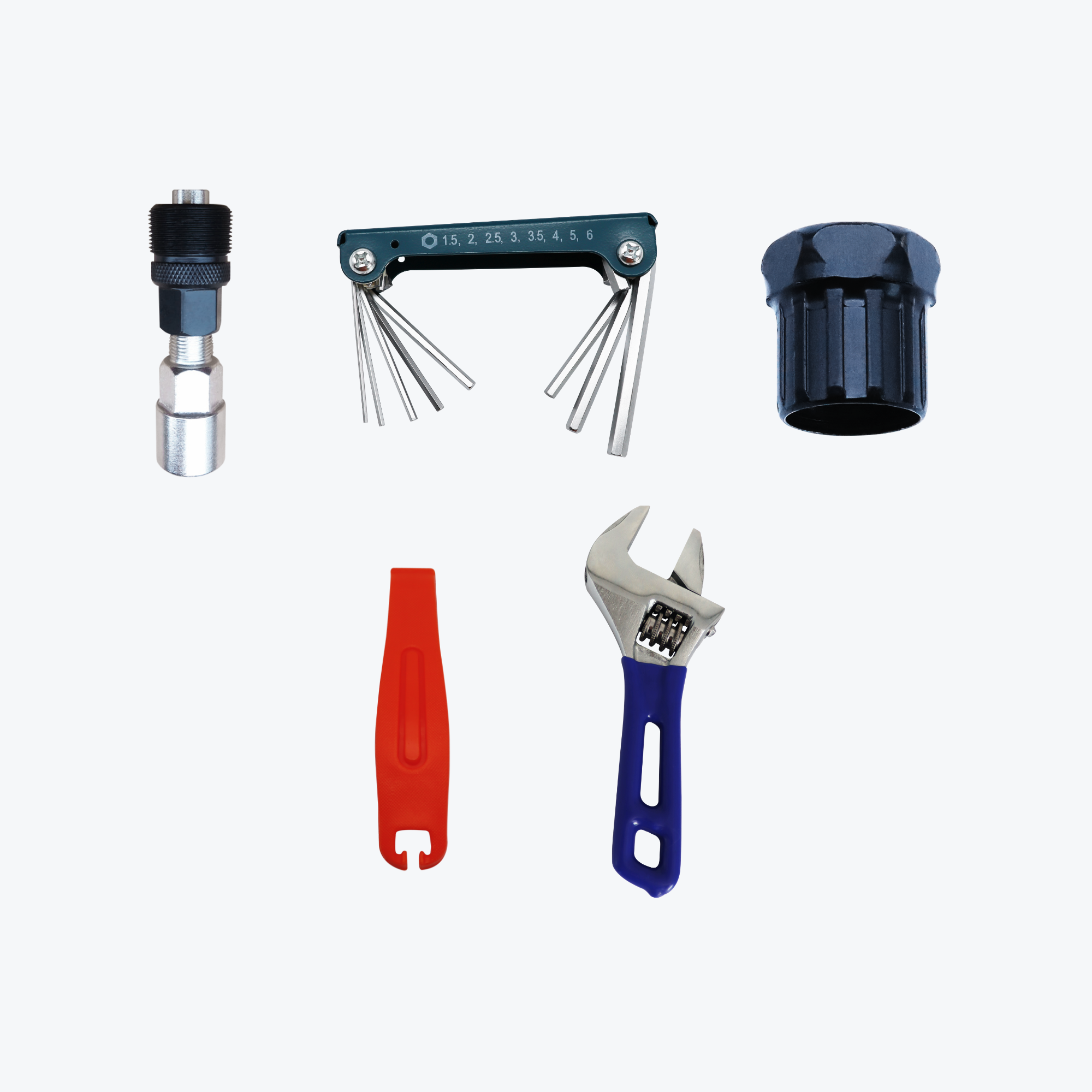
Essential Tools Required:
Hub Motor Installation:
- Quality Allen key set (4mm, 5mm, 6mm)
- Adjustable wrench or pedal wrench (15mm)
- Cassette removal tool (included with kit)
- Chain whip (included with kit)
- Tire levers
- Torque wrench (recommended)
- Cable ties and cutters
- Electrical tape
Mid-Drive Installation:
- All hub motor tools plus:
- Bottom bracket removal tool
- Crank puller tool
- Additional Allen keys for crank bolts
Tool Quality Matters:
- Use proper-sized tools only
- Avoid rounded or worn tools
- Invest in quality Allen keys
- Consider torque wrench for critical fasteners
- Replace damaged tools immediately
Motor Installation Mistakes

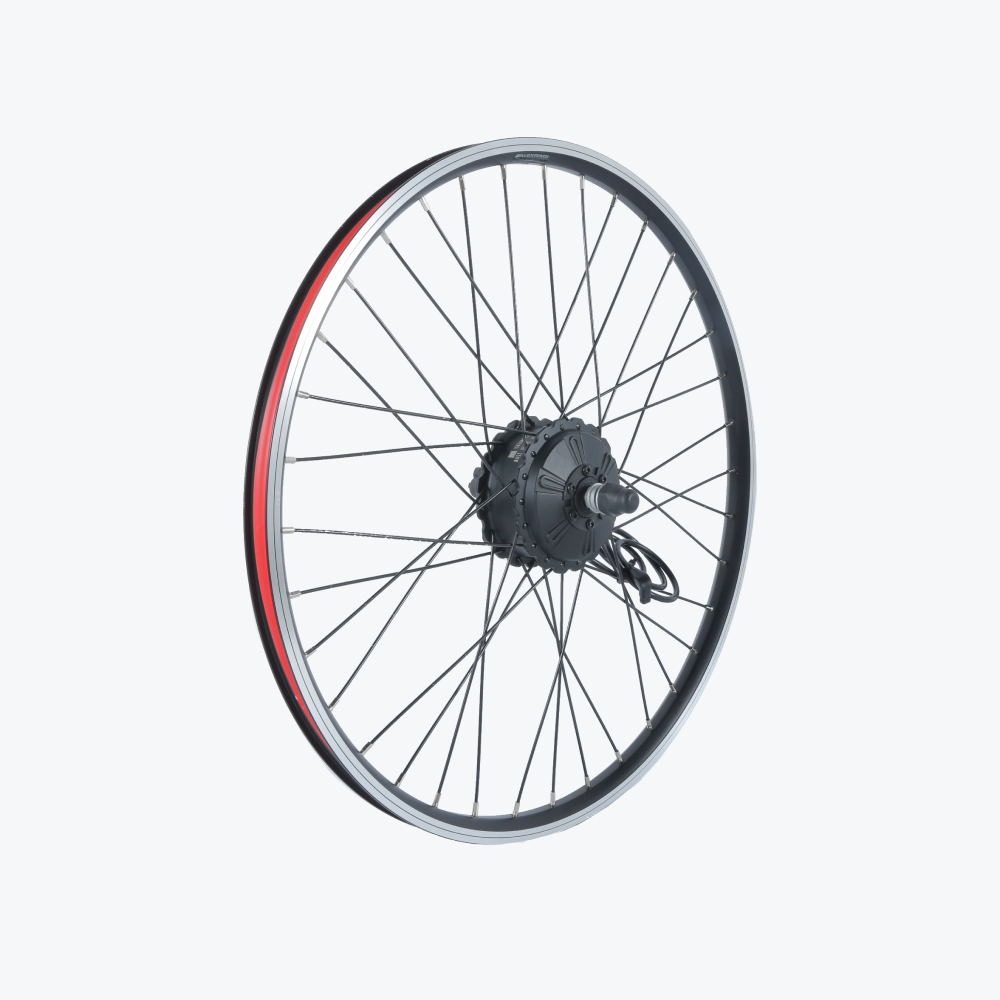
Mistake #4: Incorrect Wheel Orientation
The Error: Installing motor wheel backwards or with cables routed incorrectly.
Problems This Creates:
- Motor cable too short to reach controller
- Brake rotor on wrong side
- Tire rotation direction incorrect
- Cable stress and potential damage
- Difficult cable management
The Solution:
Proper Hub Motor Orientation:
For rear wheel motors:
- Motor cable exits on non-drive side (left side)
- Check cable length before full installation
- Verify brake rotor position matches caliper
- Confirm cassette threads onto motor properly
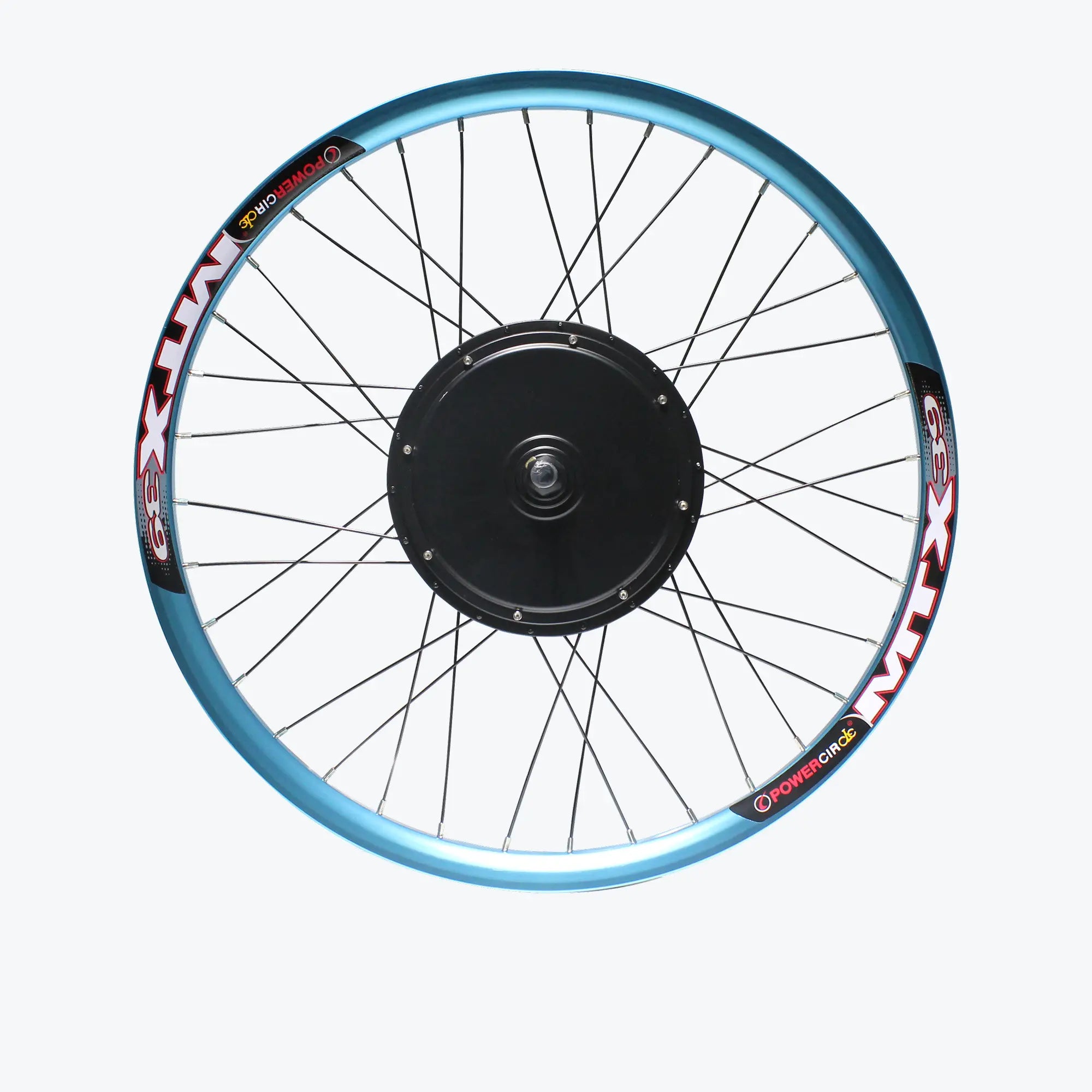
Mistake #5: Missing or Improperly Installed Torque Arms
The Error: Omitting torque arms entirely or installing them incorrectly—one of the most dangerous installation mistakes.
Why This Is Critical:
Torque arms prevent motor axle rotation under power by:
- Transferring motor torque to frame
- Preventing dropout damage
- Protecting frame integrity
- Ensuring safe operation
Frame Damage Risk:
- Aluminum frames especially vulnerable
- Dropouts can crack or deform
- Frame failure possible under power
- Dangerous sudden failures
- Expensive frame replacement
The Solution:
Proper Torque Arm Installation:
Minimum Requirements:
- One torque arm for motors under 750W
- Two torque arms for motors 1000W and above
- Both sides for high-power systems (2000W+)
Installation Procedure:
- Clean dropout area thoroughly
- Position torque arm flush against dropout
- Insert through axle
- Connect to frame or fork
- Tighten all fasteners to specification
- Verify no movement possible
- Recheck after first ride
Mistake #6: Improper Axle Tightening
The Error: Over-tightening or under-tightening motor wheel axle nuts.
Consequences:
Over-tightening:
- Damaged dropout threads
- Bent axle
- Crushed bearings
- Difficult removal
- Frame damage
Proper Tightening Procedure:
The electric bike kit battery systems include specific torque specifications:
General Guidelines:
- Use gradual, even pressure
- Tighten nuts alternately (left-right-left-right)
- Check manufacturer's torque specifications
- Use torque wrench for precision
- Verify wheel centered in frame/fork
Battery and Controller Installation Mistakes

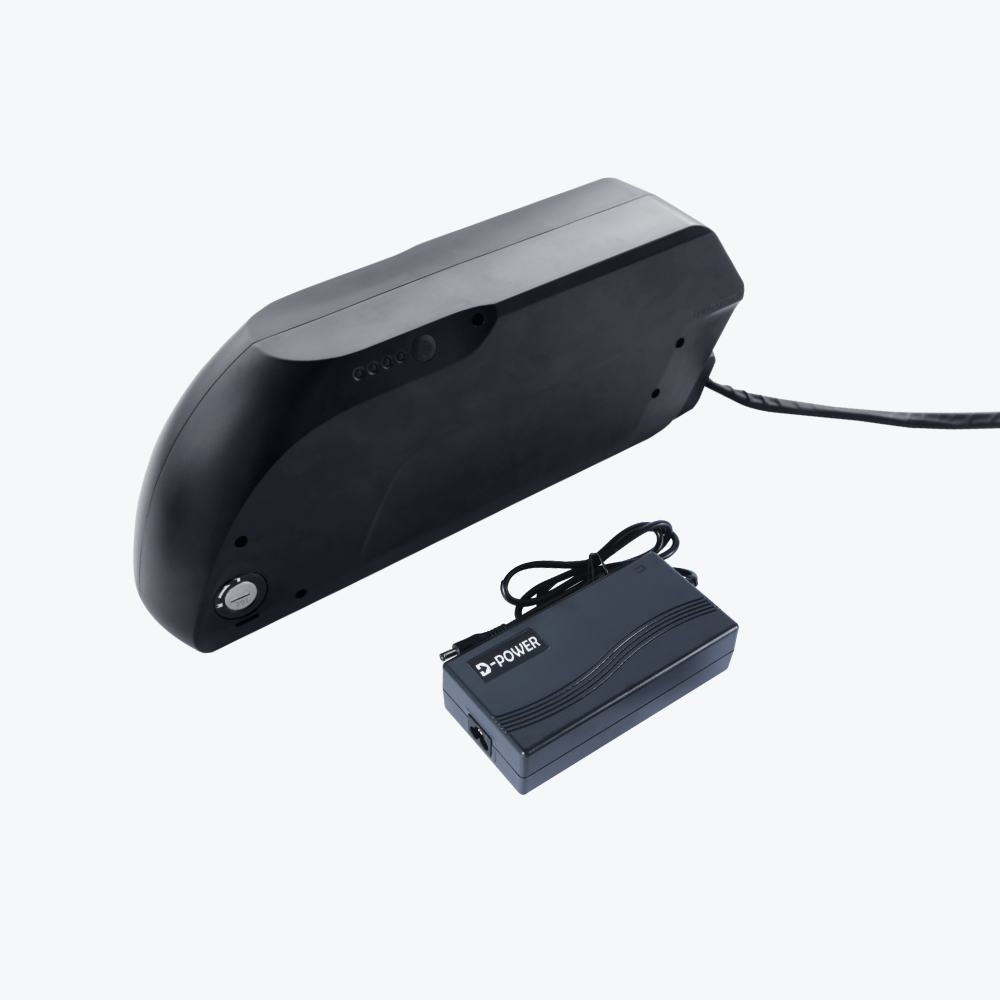
Mistake #7: Poor Battery Mounting Location
The Error: Mounting battery where it interferes with riding, creates imbalance, or risks damage.
Problems Created:
- Knee interference while pedaling
- Poor weight distribution
- Cable strain
- Difficult battery removal
- Increased damage risk
The Solution:
Optimal Battery Placement:
Down Tube Mounting (Most Common):
- Center of gravity low and central
- Easy access for removal
- Protected from impacts
- Cable routing straightforward
- Doesn't interfere with riding
Installation Best Practices:
- Use all provided mounting bolts
- Verify bottle cage holes alignment
- Check pedal clearance (especially at full lock)
- Ensure cable can reach without tension
- Test battery removal/installation ease
- Confirm lock mechanism functions
Mistake #8: Neglecting Cable Management
The Error: Leaving cables loose, unsecured, or routed where they can snag, rub, or get damaged.
Consequences:
- Cable wear from rubbing
- Snagging on obstacles
- Water ingress at connections
- Unprofessional appearance
- Potential short circuits
- Safety hazards
The Solution:
Professional Cable Management:
Routing Principles:
- Follow natural frame lines
- Avoid moving parts (cranks, wheels)
- Prevent rubbing on tire
- Keep away from heat sources
- Allow handlebar turning clearance
- Protect from water spray
Mistake #9: Reversed Motor Cable Connections
The Error: Connecting motor phase wires in wrong sequence, causing motor to run backwards or inefficiently.
Symptoms:
- Motor runs opposite direction
- Reduced power output
- Controller errors
- Abnormal noises
- Poor performance
The Solution:
Proper Connection Procedure:
Most modern systems use keyed connectors preventing incorrect connection, but if issues arise:
Diagnosis:
- Power system and test throttle
- Observe wheel rotation direction
- Check for error codes on display
- Verify smooth operation
Correction (if needed):
- Disconnect motor phase wires
- Swap any two of three phase wires
- Test operation
- If still incorrect, try different combination
- Secure properly once correct
Display and Control System Mistakes

Mistake #10: Incorrect Sensor Installation
The Error: Improperly installing or aligning pedal assist sensor (PAS) or failing to secure properly.
Problems This Creates:
- No pedal assist function
- Inconsistent assist activation
- Delayed motor response
- Assist remains on constantly
- Premature component wear
The Solution:
Cadence Sensor Installation:
Disc-Type PAS:
- Mount sensor bracket on left crank side
- Position sensor head near bottom bracket
- Install sensor disc on crank arm or pedal spindle
- Align with 2-3mm gap between disc and sensor
- Secure all fasteners
- Test rotation—no rubbing
Magnet-Type PAS:
- Install sensor on chainstay
- Mount magnet on crank arm
- Align for proper gap (typically 5mm)
- Verify clearance throughout pedal rotation
- Test sensor detection
Mistake #11: Display Mounting Issues
The Error: Mounting display where it's difficult to read, interferes with controls, or is vulnerable to damage.
Consequences:
- Poor visibility while riding
- Difficult button access
- Cable strain
- Collision with knees
- Weather exposure
The Solution:
Optimal Display Placement:
Position Criteria:
- Easily visible while riding
- Buttons accessible without hand repositioning
- Doesn't interfere with brake/shift levers
- Protected from direct impact
- Cable reaches without tension
- Secure mounting
Mistake #12: Brake Sensor Omission
The Error: Failing to install brake cut-off sensors or installing them incorrectly—a serious safety issue.
Safety Risk: Motor continues running when braking, causing:
- Extended stopping distances
- Loss of control
- Brake system overload
- Accident risk
- Legal liability
The Solution:
Mandatory Brake Sensor Installation:
Installation Procedure:
- Remove existing brake levers (if replacing)
- Install new levers with integrated sensors
- Connect brake sensor cables to controller
- Adjust lever reach for comfort
- Route cables cleanly
- Test extensively before riding
Verification Testing:
- Power system on
- Engage throttle or pedal assist
- Pull brake lever
- Motor should cut immediately
- Test both front and rear
- Verify quick response
Critical Safety Check:
- Test at low speed initially
- Verify instant motor cutoff
- Check both brakes independently
- Test in various assist levels
- Confirm consistent operation
Electrical System Mistakes

Mistake #13: Ignoring Waterproofing
The Error: Failing to properly seal electrical connections or exposing components to water intrusion.
Long-Term Consequences:
- Corrosion of connections
- Intermittent failures
- Short circuits
- Component damage
- Fire risk
The Solution:
Waterproofing Best Practices:
Connection Protection:
- Ensure all connectors fully engaged
- Verify rubber seals properly seated
- Apply dielectric grease to connections
- Use electrical tape on suspect areas
- Position connectors away from direct spray
- Route cables to drain water away
Component Positioning:
- Controller in protected location
- Battery connectors facing down when possible
- Display angled to shed water
- Sensors protected from direct spray
Maintenance:
- Inspect connections regularly
- Clean and reapply dielectric grease annually
- Replace damaged connector seals
- Check for corrosion
- Address any water ingress immediately
Pre-Ride Testing Checklist:
|
Test |
Procedure |
Pass Criteria |
|
Power On |
Turn on battery and display |
Display illuminates, no errors |
|
Throttle |
Lift rear wheel, test throttle |
Smooth acceleration, proper direction |
|
Brake Cutoffs |
Engage motor, pull brakes |
Instant motor cutoff both sides |
|
Pedal Assist |
Pedal forward in each level |
Smooth engagement, appropriate power |
|
Display Functions |
Check all buttons and menus |
All functions respond correctly |
|
Battery Reading |
Verify charge level display |
Accurate indication |
|
Lights |
Test headlight and brake light |
Proper operation if equipped |
|
Sensors |
Verify all sensor functions |
Proper detection and response |
Initial Ride Testing:
- Start in safe, open area
- Test low assist levels first
- Verify braking effectiveness
- Check handling changes
- Test all assist levels progressively
- Verify range estimation
- Check for unusual noises
- Monitor battery consumption
Mistake #16: Ignoring Torque Specifications
The Error: Guessing at proper tightness instead of following specified torque values.
Component Risk:
Critical Fasteners:
- Motor axle nuts
- Torque arm bolts
- Battery mounting bolts
- Crank bolts (mid-drive)
- Bottom bracket (mid-drive)
- Cassette lockring
The Solution:
Torque Specification Guidelines:
While specific values vary by component:
General Ranges:
- Motor axle nuts: 35-40 Nm typical
- Torque arm bolts: 15-20 Nm typical
- Battery bolts: 5-8 Nm typical
- Crank bolts: 35-40 Nm typical
- Cassette lockring: 40 Nm typical
Best Practices:
- Invest in quality torque wrench
- Follow manufacturer specifications exactly
- Tighten in proper sequence
- Recheck after first 50km
- Document all torque values applied
Conclusion
Avoiding these common installation mistakes ensures your e-bike conversion delivers safe, reliable, high-performance electric assistance for years. The 20-minute hub motor or 30-40 minute mid-drive installation becomes straightforward when you prepare properly, follow instructions carefully, and take time to do each step correctly.
Quality mid motor electric conversion kit systems from reputable manufacturers include everything needed for success—but installation quality determines actual performance and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the most critical mistake to avoid when installing an e-bike conversion kit?
Missing or improperly installing torque arms represents the most dangerous mistake, risking frame damage and sudden failure. Always install minimum one torque arm for motors under 750W, two for 1000W+ systems. Verify they're secured properly and cannot rotate—this single component prevents thousands in frame damage and serious safety hazards.
How tight should motor axle nuts be?
Follow manufacturer torque specifications (typically 35-40 Nm) using a torque wrench. Over-tightening damages dropouts and bearings, while under-tightening allows movement causing brake issues and safety hazards. Tighten gradually alternating sides, verify wheel centering, and recheck after 50km of riding for optimal security.
Do I really need to install brake cut-off sensors?
Absolutely—brake sensors are mandatory safety components that instantly cut motor power when braking. Without them, the motor continues running while braking, extending stopping distances dramatically and creating dangerous loss of control scenarios. Test both brake sensors thoroughly before riding to verify instant motor cutoff.
What's the correct gap for pedal assist sensors?
Maintain 2-3mm gap between disc-type PAS sensor head and sensing disc. Too close causes rubbing and sensor damage, too far prevents detection and eliminates pedal assist. Verify clearance throughout complete pedal rotation, secure all mounting hardware, and test sensor response before riding.
How do I know if my cables are routed correctly?
Proper cable routing follows natural frame lines, avoids moving parts (wheels, cranks), prevents rubbing on tires, allows handlebar turning clearance, and secures every 15-20cm with cable ties. Verify no tension on connections, protection from water spray, and professional appearance. Test full handlebar movement before riding.
Should I test the system before my first ride?
Comprehensive pre-ride testing is essential: lift rear wheel and test throttle for proper rotation, verify both brake sensors cut motor instantly, test all pedal assist levels, check display functions, ensure no unusual noises, and verify battery readings accurate. Initial ride should be in safe, traffic-free area testing progressively.
What should I do if I make a mistake during installation?
Stop immediately, don't force anything, and refer to instructions or videos. Disassemble back to last known good state, identify the error, correct it properly, and proceed systematically. Contact manufacturer support if uncertain—better to ask than damage components or create safety hazards. Document issues for future reference.